Dimensions
Cross-laminated timber is intended for use as a structural or non-structural element of buildings and wooden structures.
The size of CLT panels is 3.5x18 m, thickness from 60 to 360 mm. Number of layers: 3-5-7-9.
Humidity: 10% (+/- 2%).
Density: 450 kg/m3 – 500 kg/m3. The strength of the glued joint between the layers: the characteristic shear joint obtained as a result of tests is 3.24 N/mm2 (ND fv,k>1.25 N/mm2).
| Number of layers | Thickness, mm | Plate construction | ||||||
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | ||
| 3 | 60 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||||
| 3 | 80 | 20 | 40 | 20 | ||||
| 3 | 90 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||||
| 3 | 100 | 30 | 40 | 30 | ||||
| 3 | 120 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||||
| 5 | 100 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||
| 5 | 120 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 30 | ||
| 5 | 140 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 160 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 180 | 40 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 200 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 140 | 20-20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 160 | 20-20 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 180 | 20-20 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 200 | 20-20 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 5 | 220 | 20-40 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40-20 | ||
| 7 | 220 | 20-40 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40-20 | ||
| 7 | 220 | 40-40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40-40 | ||
| 7 | 260 | 40-40 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40-40 | ||
| 7 | 280 | 40-40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40-40 | ||
| 7 | 300 | 40-40 | 30 | 40-40 | 30 | 40-40 | ||
| 7 | 320 | 40-40 | 40 | 40-40 | 40 | 40-40 | ||
| 9 | 280 | 20-40 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 40-20 |
| 9 | 340 | 40-40 | 40 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40 | 40-40 |
| 9 | 360 | 40-40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40-40 |
Boards: strength class according to EN 338 ≥ T10 or ≥ C16. Thickness t 20–43 mm. Width b 105–204 mm. The ratio of the width b to the thickness t of the non-extreme glued transverse layers b/t ≥ 4:1. Moisture content of wood according to EN 13183-2 10% (+/- 2%). Within one cross-glued panel, the difference in humidity between individual boards should not exceed 5 %. Toothed connections 20–43 mm.
| Characteristic | Dimensions and specifications |
| Cross-glued timber panel | |
| Thickness | 60–360 mm |
| Thickness tolerance | ± 1 mm |
| Width | ≤ 3,50 m |
| Width tolerance | ± 3 mm |
| Length | ≤ 18,00 m |
| Length tolerance | ± 3 mm |
| The number of layers | 3 ≤ n≤ 9 |
| The number of consecutive layers with the same fiber direction | ≤ 3 for n ≥ 5 |
| The maximum width of gaps between adjacent | 2 mm |
| boards in longitudinal or transverse layers | |
| Boards | |
| Coniferous | wood material |
| Strength class according to EN 338 | ≥ T10 or ≥ C16 |
| Thickness t | 20–43 mm |
| Width b | 105–204 mm |
| The ratio of the width b to the thickness t of the non-extreme glued transverse layers | b/t ≥ 4:1 |
| Moisture content of wood according to EN 13183-2 | 8–14% . Within one cross-glued panel, the difference in humidity between individual boards should not exceed 5%. |
| Toothed joints | According to DSTU EN 14080:2019 (EN 14080:2013, IDT) |
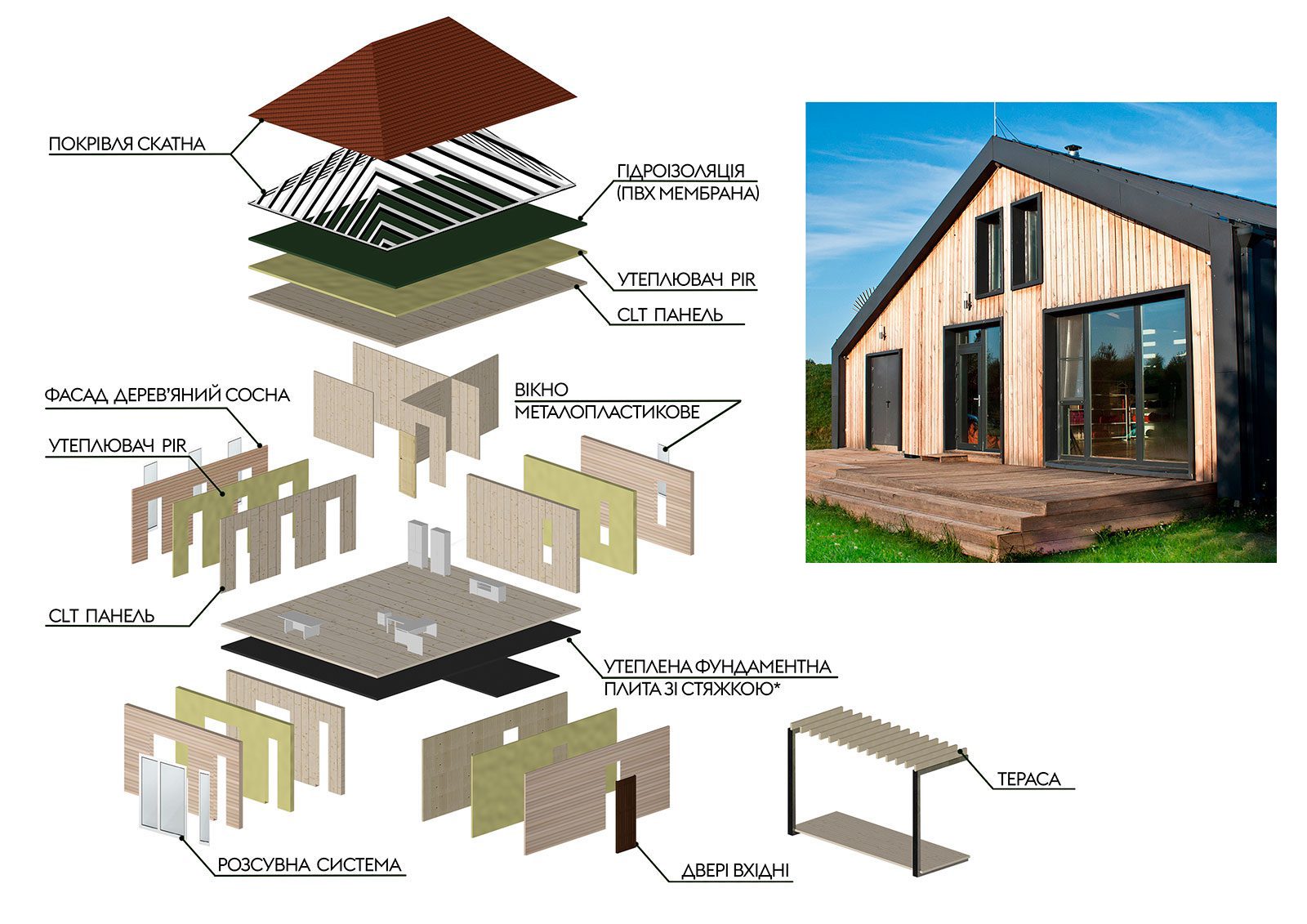
House installation example
Fire resistance
CLT panels comply with all fire building regulations. Due to the slow charring and transverse arrangement of the layers of wood, effective fire protection is provided. Fire resistance is the time during which the structure resists the influence of fire, while maintaining the calculated load-bearing capacity. The fire resistance rating refers to the time a building component can withstand during a fire and damage to its integrity.
CLT has an estimated charring rate of approximately 0.7 mm/min. The charred layer, which is formed during combustion, acts as an insulator for the inner layers, thereby protecting the structural elements from further loss of strength. The most vulnerable component of this system, as a rule, is the connecting elements, due to the rapid decrease in the strength of steel at high temperatures.
To counteract this, it is necessary that all connecting elements are inside the wood or covered with fire-resistant paint. Additional protection is provided by the coating. Each additional 16 mm plasterboard adds approximately 40 minutes of increased fire resistance. Each layer of plasterboard, 13 mm thick, adds approximately 25 minutes of protection.
Fire Safety (BWR2)
Reaction to fire:
Euroclass D-s2, d0
Resistance to fire:
Euroclass Dfl-s1
Burnout rate 3):
β0 = 0.65 mm/min
βn = 0.7 mm/min
Test result:
M0, M0 1GK, REI 60, REI 120
Thermal conductivity is 0.13 W/mK, compared to concrete, which has 1.4 W/mK
Energy saving and heat retention BWR6, DSTU B EN 10077-2:2022.
CLT has a relatively high heat capacity (thermal inertia). It is typically around 2100 J/kg°C compared to concrete which is around 880 J/kg°C.
This program provides an opportunity to quickly evaluate the following parameters:
- thermal conductivity
- impact on the environment
- moisture insulation parameters, dew points
- thermal protection (protection against the influence of solar radiation)
For various options for the layout (location) of layers of heat insulation, noise insulation, moisture protection, decoration, etc. for various building construction elements (wall, ceiling, floor, ceiling, covering).
Load
| Construction weight, kg | Temporary loads, kg | The span of the plate, fastened on two sides | ||||||||
| 100 | 3m | 3,5m | 4m | 4,5m | 5m | 5,5m | 6m | 6,5m | 7m | |
| 90 | 80 L3s (30-20-30) | 80 L3s (30-20-30) | 100 L3s (40-30-40) | 120 L3s (40-40-40) | 120 L3s (40-40-40) | 140 L5s (40-20-20-20-40) | 160 L5s (40-20-40-20-40) | 160 L5s (40-20-40-20-40) | 180 L5s (40-30-40-30-40) | |
| 195 | 90 L3s (30-30-30) | 140 L5s (40-20-20-20-40) | 180 L5s (40-30-40-30-40) | 200 L5s (40-40-40-40-40-40) | ||||||
| 240 | 100 L3s (40-30-40) | 120 L3s (40-40-40) | 140 L5s (40-20-20-20-40) | 160 L5s (40-20-40-20-40) | 180 L5s (40-30-40-30-40) | 200 L5s (40-40-40-40-40-40) | 220 L7s (40*4+20*3) | |||
| 360 | 90 L3s (30-30-30) | 160 L5s (40-20-40-20-40) | 220 L7s (40*4+20*3) | |||||||
| 480 | 100 L3s (40-30-40) | 120 L3s (40-40-40) | 140 L5s (40-20-20-20-40) | 180 L5s (40-30-40-30-40) | 200 L5s (40-40-40-40-40-40) | 240 L7s (40*4+30*2+20) | ||||
| 600 | 160 L5s (40-20-40-20-40) | 180 L5s (40-30-40-30-40) | 200 L5s (40-40-40-40-40-40) | 220 L7s (40*4+20*3) | 240 L7s (40*4+30*2+20) | 260 L7s (40*5+30*2) | ||||
Questions/Answers
What are CLT panels?
CLT (Cross-Laminated Timber) is a solid wooden panel, which consists of cross-positioned, glued together, layers of coniferous wood. CLT is a unique building material that confidently competes with steel and concrete. It is environmentally friendly and energy efficient, with high strength and rigidity.
Where are CLT panels manufactured?
CLT panels and constructions from them are produced by LLC "Ukrainian Holding Sawmill Company" under the СLT REZULT brand. The sawmill company is among the TOP 10 largest sawmills in Eastern Europe. Our industrial park is 200 hectares, the volume of processed wood per year is more than 1.2 million cubic meters, 95% of our products are exported to 45 countries of the world. The annual production capacity of CLT is 91 thousand cubic meters, which is 7.5 thousand cubic meters per month. Production facilities: 11-B, Serhiya Kemskoho str., 11501, Korosten, Zhytomyr Region, Ukraine.
How are the panels produced?
Boards for CLT, made of pine, are dried, finger-jointed along their length, laid in layers, on which glue is applied. After this - the stage of gluing in the press, the next stage is grinding. Then door and window openings are made in them, and channels and platforms are milled for the laying of various communications. All this happens on CNC machining centers with high precision. For these processes, the equipment of the world's leading manufacturers Ledinek and Hundegger is used. Type 1 glue (PUR) is used in production - a one-component liquid polyurethane glue that does not contain formaldehydes, according to EN 301, EN 15425, and solvents harmful to health.
What size are CLT panels?
The size of CLT panels is 18 m in length and 3.5 m in width, thickness from 60 to 360 mm.
Number of layers: 3-5-7-9.
Humidity: 10% (+/- 2%).
Density: 450 kg/m3 3 – 500 kg/m3.3.
Panels at the factory are cut according to the architectural project, and can be of different sizes and thicknesses.
Is CLT technology more economical than other construction methods?
Yes, the CLT technology is more economical due to: reduction of the foundation, as CLT is lighter than traditional building materials; increase in usable area due to smaller wall thickness; finished interior decoration - finishing CLT; speed - the house is assembled from ready-made parts, cost savings due to reduced construction time, fewer workers and mechanisms; ready-made slots and strobes for communications; possibilities of completion of ready-made structures.
Where are CLT panels used?
In the construction of one-storey and multi-storey buildings for individual and multi-apartment housing, as well as public premises (hotels, schools, barracks, dormitories, hospitals, etc.) as quickly constructed structures. Also during the reconstruction or completion of the upper floors of the building, which is possible due to the lightness of the structures.
Are CLT panels certified?
Yes, the quality of CLT Rezult products is confirmed by certificates that confirm fire resistance, durability and environmental friendliness.
How many floors can be built with CLT?
In Europe, many residential and public buildings are built from CLT panels.
СLT is both a strong and resilient material, which allows us to easily add additional floors – for example, a 100 mm thick, 2500 mm high panel can hold more than 120 tons. World engineers and designers have conducted a number of studies and calculations, establishing that even skyscrapers can be built from such panels, for example – up to 44 floors high (the project is being built in Chicago). Also, CLT panels are used for the construction of private, one-storey houses and complex architectural projects.
What is the lifespan of a house built with CLT?
With the right construction methods, the service life can be very long. Using the example of old wooden houses, it becomes clear that a service life of several hundred years is not uncommon. And with modern technologies, houses are even more stable and reliable. In Europe, this technology is considered advanced, so Europeans build important buildings for cities with a long service life in mind.
Does CLT attract moisture and mold?
No, only poorly dried and improperly treated wood can attract moisture, because it condenses on a surface that has a lower temperature compared to the surrounding air. In contrast, all CLT wood is dried to a moisture content of 10% (+/- 2%) and remains in its natural state ‒ "breathing" as it does in nature. This means that your CLT house can absorb any moisture from the environment in a balanced way and release it again when the air becomes dry, balancing between +2% -2%.
Are CLT panels fireproof?
СLT copes exceptionally well with fires, thanks to the slow charring and self-insulating properties of the wood, which provides effective fire protection. The fire resistance rating refers to the time that a building component can withstand during a fire and a violation of its integrity. CLT has an estimated charring rate of approximately 0.7 mm/min. The charred layer, which is formed during combustion, acts as an insulator for the inner layers, thereby protecting the structural elements from further loss of strength.
What is the history of CLT?
The development of CLT technology occurred in the early 1990s in Switzerland.
In 1996, a joint study was conducted in Austria, which resulted in the emergence of the term CLT (Cross-Laminated Timber).
In the early 2000s, the use of CLT in construction has increased significantly and it is now a common construction method in Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Sweden, Norway and the UK. North America is also beginning to use CLT extensively in construction.
And in Ukraine, this is a new technology that the CLT Rezult company began to implement.
Is wood warping and shrinkage a problem in CLT buildings?
No. The perpendicular-to-transverse arrangement of the wood fibers in CLT ensures a very stable panel size, eliminating any significant warping or shrinkage. This is the main difference between ordinary wooden panels made of solid wood and traditional wooden frame systems.
What are the acoustics like in CLT buildings?
The acoustic characteristics of CLT are excellent and equivalent to other construction methods.
Cross-laminated wood allows you to achieve high sound-insulating acoustic characteristics, both for the ceilings and for the walls.
As with other forms of construction, the acoustics of CLT are not entirely dependent on the base material. To ensure the necessary acoustic performance, a combination of elements covering the walls or ceiling is used.
Is a CLT building thermally better than steel or concrete?
Yes. Wood is a poor heat conductor, which means it is a good heat insulator. Low natural thermal conductivity (0.13 W/mK) and high heat capacity (2.10 kJ/kg). Steel and concrete, on the other hand, are good conductors, which means they give off more heat. An additional advantage of CLT is that the precise nature of the manufacturing process ensures no air leakage. Therefore, the desired air temperature is maintained inside the building and is not lost to the outside environment, which applies equally to both cooling and heating.
Can CLT be used for buildings other than residential?
Yes. CLT has already been used to create various types of buildings, including schools, kindergartens, offices, shopping centers, medical facilities, sports complexes, museums, government buildings and others.
Can CLT be used for the construction of private houses?
Yes. The construction of single-storey or low-rise buildings using CLT is extremely popular in Europe and is considered a premium product in the market.
How does using CLT improve the quality of your building?
The high-precision production of CLT parts ensures a tighter sealing of building structures, which guarantees better overall thermal characteristics. Lightweight CLT construction does not require a strong foundation. Quickly mounted. You can use any decoration of the facade and walls. And most importantly, it is an ecologically clean house with the possibility of preserving the beauty of the texture of natural wood.
How does a CLT building behave under earthquakes and other loads?
A well-designed wooden building performs much better than a concrete building under earthquakes and other loads. Buildings with CLT are very resilient and good at dissipating energy, which also depends heavily on the mechanical connections used during construction.
Recent tests of multi-storey CLT construction by Trees and Timber (the Italian Research Institute in Japan) have found that the structure performs extremely well under severe earthquake conditions. The building that was used in the test in Japan was later dismantled and reconstructed in Italy for permanent use.
What wood is used in CLT production?
Pine, which is supplied from ecologically clean forests of Ukraine, and has an FSC certificate.
Wood is the only sustainable construction material that stores carbon throughout its life cycle. Forestry works in such a way that young trees are planted instead of old ones being harvested.






